How to develop IE add-on in VB.NET, C#, C++
for Internet Explorer 6 - IE11
|
Add-in Express™ Add-in Express Home > Add-in Express for Internet Explorer > Online Guide > Programming Internet Explorer addons Creating an IE add-on projectMake sure that you have administrative permissions before running Visual Studio. Also, if you have Windows Vista, Windows 7, Windows 8, or Windows 10, run Visual Studio via Run as Administrator. In Visual Studio, open the New Project dialog and navigate to the Extensibility folder.
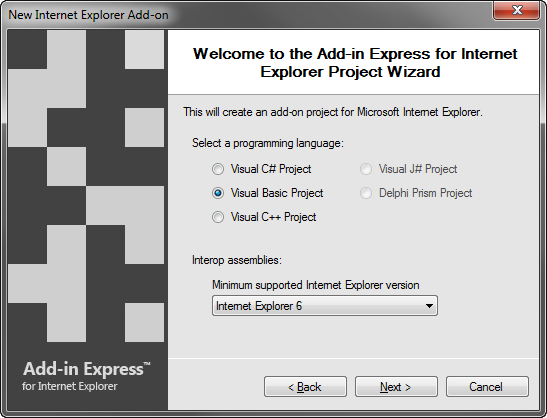
Choose Add-in Express IE Add-on and click OK. This starts the IE Add-on project wizard. Then choose your programming language and the minimum Internet Explorer version that you want to support and click Next.
Choosing a particular Internet Explorer version will add corresponding interop assemblies to the project. Later on, in case you need to support an older or a newer IE version, you will be able to replace interop assemblies and reference them in your project. If you are in doubt, choose Internet Explorer 6 as the minimum supported Internet Explorer version and your add-in will work in all versions, from IE6 to IE11. If you need background information, see What are interop assemblies?.
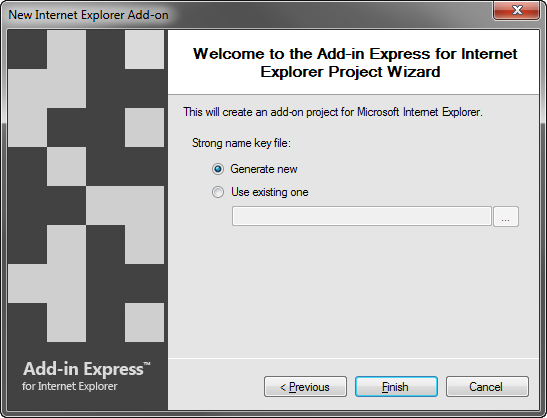
If you don't know anything about strong names or don't have a special strong name key file, choose Generate new. If you are in doubt, choose Generate new. If you need to use a specific strong name key file at a later point of time, you will be able to specify its name on the Signing tab of your project properties; you are required to unregister your toolbar project before using another strong name. Choose Generate new or specify an existing .snk file and click Next. The project wizard creates and opens a new solution in Visual Studio.
The solution contains the only project, IE add-on project. The project contains the IEModule.vb (or IEModule.cs) file discussed in the next step. IE ModuleIEModule.vb (or IEModule.cs) is the core part of the project. It is a container for components essential for the functionality of your add-on. You specify add-on properties in the module's properties, add the components to the module's designer, and write the functional code of your add-on in this module. To review its source code, in the Solution Explorer, right-click IEModule.vb (or IEModule.cs) and choose View Code in the popup menu.
In the code of the module, pay attention to the following points:
IE Module designerIn the Solution Explorer, right-click the IEModule.vb (or IEModule.cs) file and choose View Designer in the popup menu.
The designer view provides access to the following three areas:
The module provides a number of properties and commands. The properties are available in the Properties window when you click the designer surface of the module. The commands are available in the context menu of the module's designer. IE add-on development in full detailsSee the following pages:
Running the Internet Explorer add-onRegister the add-on and restart IE. To register the add-on, choose Register Add-in Express Project in the Build menu. Debugging the Internet Explorer add-onTo debug an IE extension, you need to use Attach to Process in the Debug menu. See How to: Attach to a Running Process. Deploying the Internet Explorer add-onNote that IE add-ons must be registered in HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE (HKLM) and, consequently, administrative permissions are required when installing an IE add-on. The table below contains links to corresponding step-by-step instructions describing installing and updating an IE add-on.
What's next?IE may run multiple windows and processes. Accordingly, multiple instances of your add-on can be created, each instance running in a different thread and even process. Check IE Essentials where we describe how to deal with this. |